Keeping Your Pup Healthy: Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Levels in Dogs

Maintaining your dog’s health goes beyond regular walks and a balanced diet—it also involves keeping a close eye on its blood sugar levels. Just like humans, dogs need stable blood glucose to stay energetic, healthy, and happy. Understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar levels in dogs, recognizing the signs of imbalances, and knowing how to maintain healthy glucose levels can make a significant difference in your pet’s well-being.
What is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the primary source of energy for your dog’s cells. It’s crucial for fueling activities, maintaining organ function, and supporting overall bodily processes. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, plays a key role in regulating blood glucose levels by helping cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
What is Normal Blood Sugar for Dogs?
Normal blood sugar levels in dogs typically fall within the following ranges:
- Fasting Blood Glucose: 70-140 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter)
- Postprandial Blood Glucose (after eating): 90-180 mg/dL
These values can vary slightly based on factors such as the dog’s age, breed, size, and overall health. Regular monitoring, especially for dogs with diabetes or other health conditions, helps ensure that blood glucose remains within this healthy range.
How is Blood Sugar Measured in Dogs?
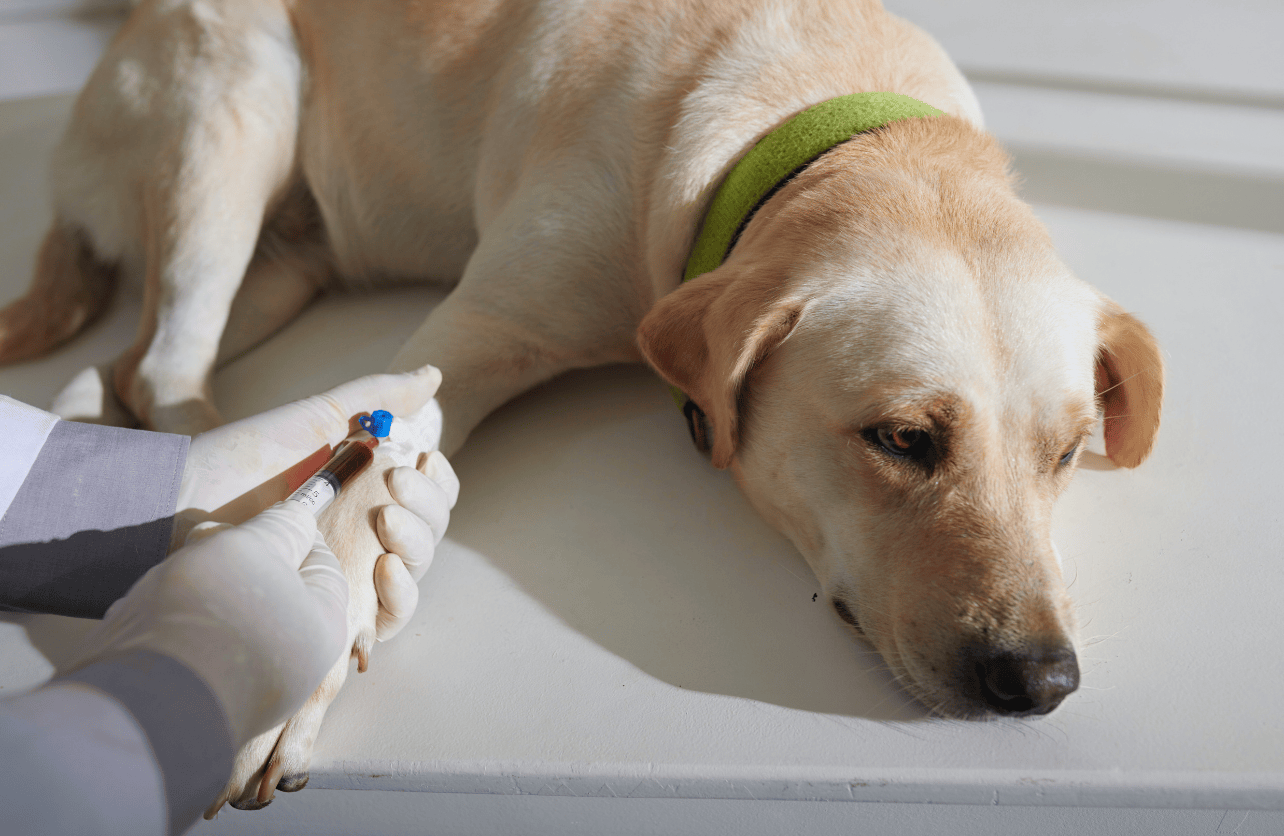
Veterinary Blood Tests
Your veterinarian can perform several types of blood tests to measure your dog’s blood sugar levels:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Part of routine check-ups, it helps in diagnosing various conditions.
- Biochemical Profile: Measures blood glucose along with other metabolic indicators.
- Fructosamine Test: Reflects average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 weeks.
Home Glucose Monitoring
For dogs diagnosed with diabetes, home monitoring is essential. This involves using a glucometer designed for pets:
- Gather Supplies: Glucometer, test strips, lancets, and a small sample of blood.
- Sample Collection: Typically from the ear or paw pad using a lancet.
- Testing: Apply the blood to a test strip inserted into the glucometer.
- Recording Results: Keep a log of daily blood glucose levels for veterinary review.
Home monitoring provides real-time data, allowing for timely adjustments to insulin dosages and dietary changes.
Signs of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels

High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
Hyperglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels exceed normal ranges. Common signs include:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: Excess glucose in the blood leads to increased water intake and frequent urination.
- Increased Hunger: Despite eating more, dogs may still feel hungry as cells are unable to utilize glucose effectively.
- Weight Loss: Occurs even if the dog has a normal or increased appetite.
- Lethargy and Weakness: High blood sugar can cause fatigue and reduced energy levels.
- Blurred Vision: May lead to cataract formation and vision impairment.
- Vomiting and Diarrhea: Gastrointestinal distress can occur in severe cases.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Hypoglycemia happens when blood glucose levels drop below normal, which can be life-threatening. Signs include:
- Weakness and Lethargy: Lack of glucose impairs muscle function and energy levels.
- Tremors and Seizures: Severe hypoglycemia can cause neurological symptoms.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Impaired brain function leads to behavioral changes.
- Loss of Consciousness: In extreme cases, hypoglycemia can result in coma or death.
- Excessive Barking or Whining: Dogs may vocalize distress when experiencing low blood sugar.
Causes of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
Hyperglycemia
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most common cause, where the body cannot produce or effectively use insulin.
- Stress: Acute stress can temporarily elevate blood glucose levels.
- Infections or Illnesses: Conditions like pancreatitis can disrupt glucose metabolism.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance.
Hypoglycemia
- Excessive Insulin Administration: Overdose of insulin in diabetic dogs can cause blood sugar to drop too low.
- Skipping Meals: Not eating enough or irregular feeding schedules can lead to hypoglycemia.
- Overexertion: Intense exercise without adequate nutrition may deplete blood glucose.
- Liver Disease: The liver plays a key role in glucose storage; dysfunction can cause hypoglycemia.
- Endocrine Disorders: Conditions affecting hormone balance can impact blood sugar levels.
Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar in Dogs

1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet tailored to your dog’s specific needs is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. For diabetic dogs, this typically involves:
- Low Carbohydrate, High Fiber Diet: Helps stabilize blood glucose by slowing glucose absorption.
- Consistent Feeding Schedule: Regular meal times help manage insulin needs and prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
2. Regular Exercise
Moderate, consistent exercise helps regulate blood sugar by improving insulin sensitivity and aiding in weight management. Avoid sudden, intense activities that could cause blood sugar spikes or drops.
3. Medications and Insulin Therapy
For diabetic dogs, adhering to prescribed insulin therapy is essential. Regular veterinary check-ups ensure that insulin dosages are appropriate based on blood glucose monitoring.
4. Home Monitoring
Frequent blood glucose monitoring at home allows for timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medications, maintaining blood sugar within the normal range.
5. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of insulin resistance and helps manage blood glucose levels effectively.
6. Stress Reduction
Minimizing stress through a calm environment, regular routines, and positive reinforcement can help prevent temporary spikes in blood sugar.
When to Consult a Veterinarian
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential, especially for dogs diagnosed with diabetes or those showing signs of abnormal blood sugar levels. Contact your vet if you observe any signs of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, or if you have concerns about your dog’s diet, exercise, or medication regimen.
Your Pet’s Best Interest, Always
At Pet Institute, we take pet care seriously. We're dedicated to transparency, impartiality, and the well-being of your pets in every article, review, and recommendation we provide. Our unwavering commitment to these principles ensures that you, our valued reader, always receive reliable and unbiased information. Let us be your trusted guide in the world of pet care and companionship.